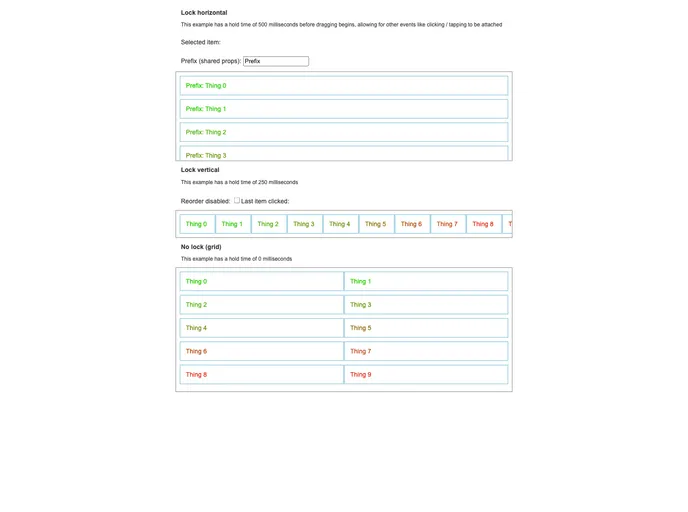
Overview
React Reorder (v2) is an innovative React component designed for creating interactive and dynamic lists or grids via drag-and-drop functionality. With its touch-enabled capabilities, it caters to users on both desktop and mobile platforms, making it a versatile solution for any React application. The component not only supports various browsers but also enhances user experience with features like auto-scrolling during dragging and customizable hold times before the drag action is initiated.
This component is particularly beneficial for developers looking to implement an intuitive reordering feature in their projects, all while maintaining compatibility with modern accessibility needs. Whether you’re building a To-Do list, photo gallery, or any sortable content, React Reorder provides a seamless experience that is both efficient and user-friendly.
Features
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Easily reorder items in a list or grid with simple drag-and-drop actions, enhancing interactivity.
- Touch Enabled: Fully supports touch devices, ensuring a smooth experience across all platforms, from desktops to smartphones.
- Auto-Scroll During Dragging: Automatically scrolls the container while dragging, making it easy to reorder items that are out of view.
- Customizable Hold Time: Set a delay before the drag begins, allowing for other events such as clicks or taps without interference.
- Compatibility: Compatible with modern browsers and extensively tested with React versions 0.14 and 0.12-0.13 for stability.
- Callback Functions: Provides callback capabilities for actions post-reorder or when items are clicked, enabling custom responses to user interactions.
- Easy Integration: Simple installation via npm or bower, making it easy to add to existing React projects.
- Unique Item Keys: Ensures that each item is identifiable by unique keys, which is essential when working with arrays of primitives.